Home » Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Remedial Action Rectification Plan for ASQA Non-Compliance

Non-compliance findings from the Australian Skills Quality Authority (ASQA) audits can be daunting, but they also present an opportunity for growth. Addressing these findings requires a structured and effective Remedial Action Rectification Plan (RARP) to not only meet ASQA’s requirements but also strengthen your Registered Training Organisation (RTO).
This blog walks you through the process of creating a compliant and practical RARP, with examples and insights to ensure your RTO is audit-ready.
A Remedial Action Rectification Plan (RARP) is a formal document outlining the steps an RTO will take to address non-compliance issues identified during an ASQA audit.
Key Objectives of a RARP:
When is a Remedial Action Rectification Plan (RARP) Required?
A robust RARP must include:
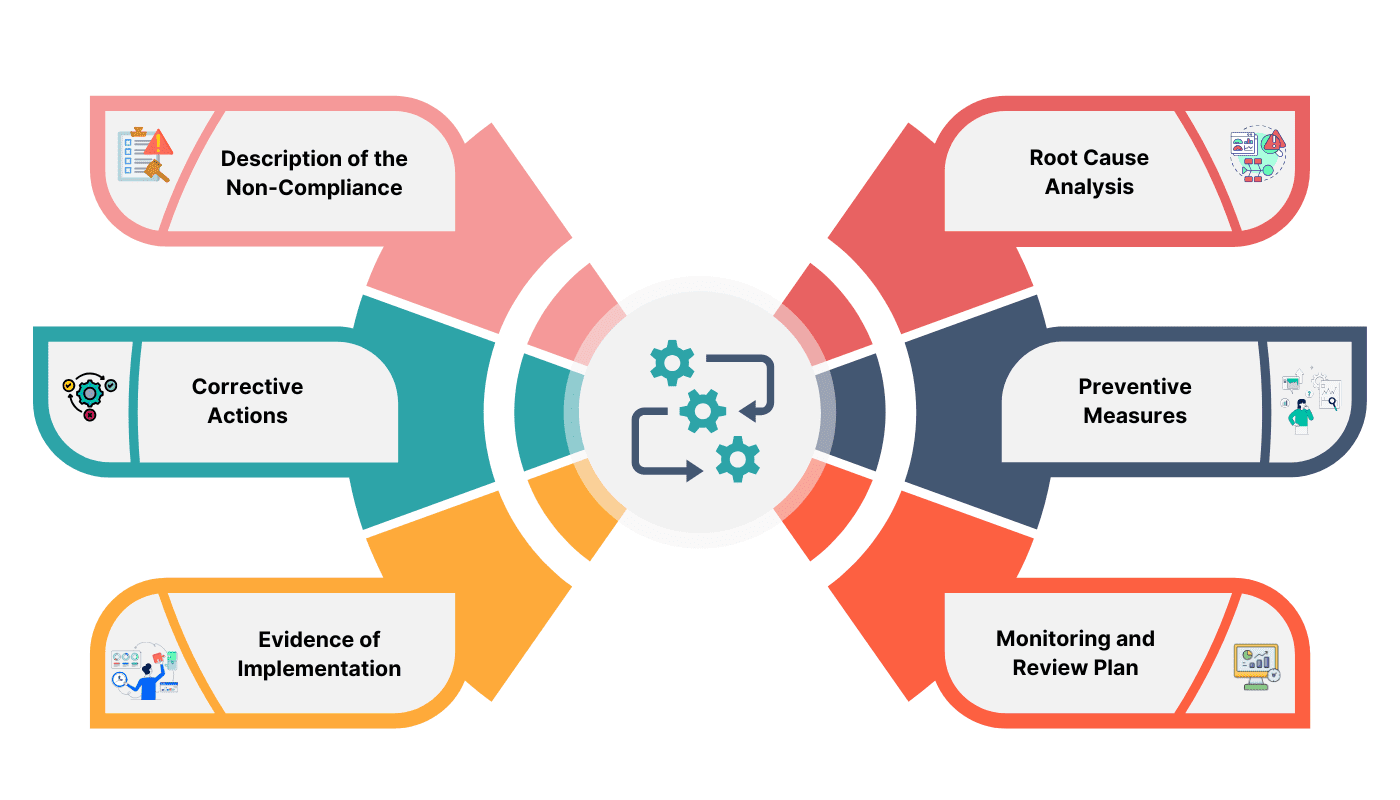
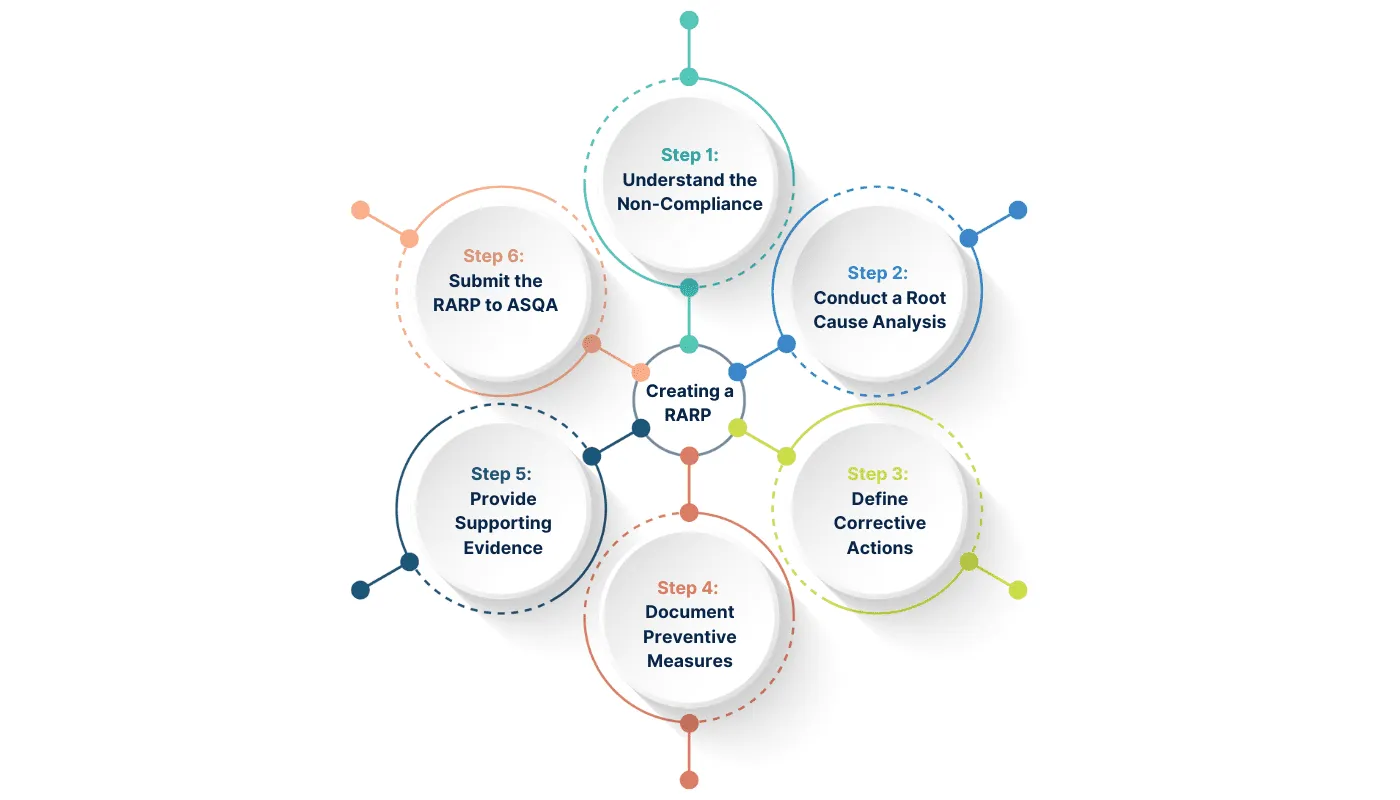
Non-Compliance Identified:
Assessment tools for the unit CHCAGE005 Provide Support to People Living with Dementia do not address all performance criteria and knowledge evidence requirements.
Root Cause Analysis:
Corrective Actions:
| Action | Timeline | Responsible Person(s) | Expected Outcome |
| Revise assessment tools to align with current training package. | 2 weeks | Compliance Officer/Trainers | Updated tools meet unit requirements. |
| Conduct validation sessions with trainers and industry representatives. | 3 weeks | RTO Coordinator | Validation feedback incorporated. |
Preventive Measures:
Evidence of Implementation:
Monitoring and Review Plan:
Creating a Remedial Action Rectification Plan is a critical step in addressing ASQA non-compliance and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By understanding the root causes, defining clear corrective actions, and implementing preventive measures, your RTO can turn audit findings into opportunities for growth.
Disclaimer:
The information presented on the VET Resources blog is for general guidance only. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee the completeness or timeliness of the information. VET Resources is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for the results obtained from the use of this information. Always consult a professional for advice tailored to your circumstances.
Ben Thakkar is a Compliance, Training, and Business specialist in the education industry. He has held senior management roles, including General Manager, with leading Registered Training Organisations (RTOs) and Universities. With over 15 years of experience, Ben brings extensive expertise across audits, funding contracts, VET Student Loans, CRICOS, and the Standards for RTOs 2025.
Ben Thakkar Linkedin
By submitting this form, you agree to the VET Resources Privacy Policy.