
Structured Workplace Learning (SWL) is a vital component of education and training that bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical experience. It is designed to provide students with the opportunity to develop skills in a real-world work environment, complementing their classroom learning. By integrating hands-on workplace experience into the learning process, SWL enhances students’ employability, understanding of industry standards, and readiness for their chosen careers.
Structured Workplace Learning plays a crucial role in preparing students for the workforce. It offers a range of benefits, not only for students but also for employers and the education system. Understanding these benefits provides a clear picture of why SWL is an essential aspect of education.
SWL allows students to gain practical experience in their field of study. They can apply classroom knowledge in real-world scenarios, enhancing their understanding and developing industry-specific skills. Students also build confidence and improve their communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities. Additionally, SWL helps students network with industry professionals, increasing their chances of securing employment after completing their studies.
Employers benefit from participating in SWL programs by accessing a pipeline of motivated, emerging talent. These programs provide an opportunity for businesses to shape the skills of future workers according to their industry needs. Employers also contribute to their community and industry by fostering the next generation of professionals.
The education system benefits from SWL by producing graduates who are better prepared for the workforce. This enhances the reputation of educational institutions and strengthens partnerships between schools, training organisations, and industry bodies.
SWL is typically integrated into a student’s curriculum. It involves planned, supervised activities that align with the learning outcomes of their course. These activities are designed to give students a deeper understanding of their chosen field and its practical applications.
A key component of SWL is work placements, where students spend time in a workplace relevant to their studies. These placements allow students to observe and participate in day-to-day operations, guided by experienced professionals. Work placements can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the course and industry requirements.
During SWL, students’ performance is assessed based on their ability to meet specific competencies and learning outcomes. Regular feedback from supervisors and mentors is essential to help students identify their strengths and areas for improvement.
SWL is typically integrated into a student’s curriculum. It involves planned, supervised activities that align with the learning outcomes of their course. These activities are designed to give students a deeper understanding of their chosen field and its practical applications.
A key component of SWL is work placements, where students spend time in a workplace relevant to their studies. These placements allow students to observe and participate in day-to-day operations, guided by experienced professionals. Work placements can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the course and industry requirements.
During SWL, students’ performance is assessed based on their ability to meet specific competencies and learning outcomes. Regular feedback from supervisors and mentors is essential to help students identify their strengths and areas for improvement.
SWL is available across a wide range of industries, ensuring students from diverse fields can benefit from real-world experience. Here are some key industries where SWL is commonly implemented:
The healthcare and aged care industries rely heavily on practical training. Students pursuing careers in nursing, allied health, or aged care can gain hands-on experience by working in hospitals, clinics, or aged care facilities. This exposure helps them understand patient care, medical procedures, and the importance of empathy and professionalism.
The construction and trades industries provide SWL opportunities for students studying carpentry, plumbing, electrical work, and similar fields. On-site experience enables students to learn safety protocols, technical skills, and the use of tools and equipment.
In hospitality and tourism, students gain practical knowledge by working in hotels, restaurants, or travel agencies. This experience helps them develop customer service skills, manage events, and understand the operational aspects of these industries.
The IT sector offers SWL placements in roles such as software development, network engineering, and cybersecurity. Students can apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world projects, gaining insights into the rapidly evolving tech industry.
Future educators and childcare professionals benefit from SWL by working in schools, daycare centres, or educational institutions. These experiences help them understand classroom management, lesson planning, and child development.
Successful implementation of SWL requires collaboration between educational institutions, employers, and students. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
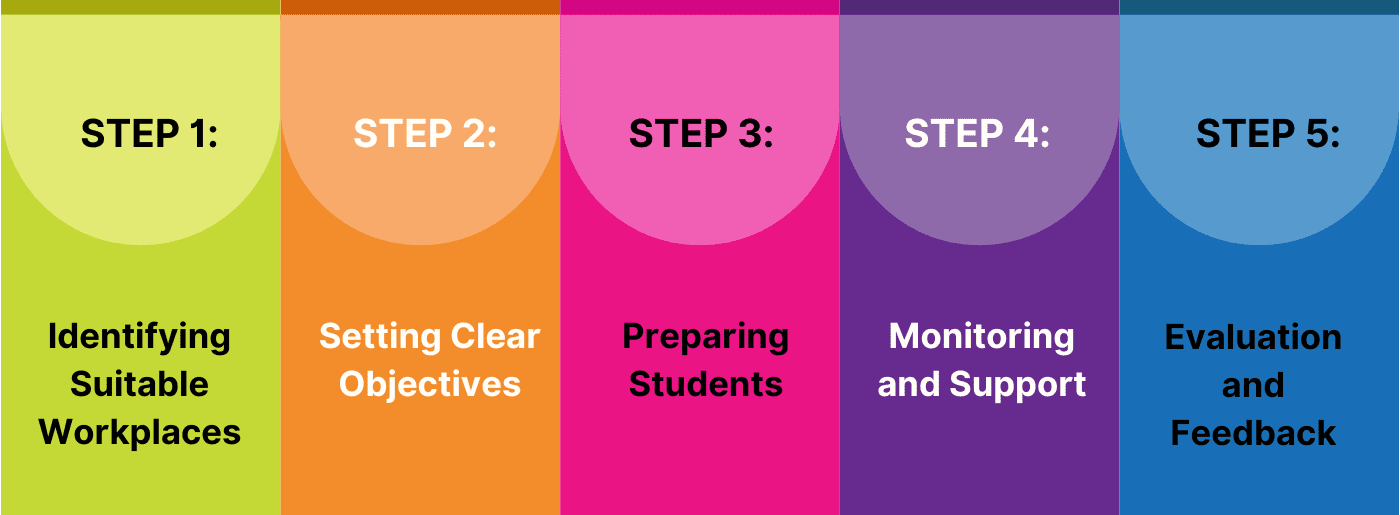
Educational institutions need to establish partnerships with businesses and organisations willing to host students. These workplaces should align with the students’ field of study and offer relevant learning opportunities.
Defining clear learning objectives ensures that SWL activities align with the curriculum. These objectives guide both students and employers, ensuring a focused and productive experience.
Before starting SWL, students should undergo orientation sessions to understand workplace expectations, safety protocols, and professional behaviour. This preparation sets the stage for a successful placement.
Regular monitoring and support from mentors, supervisors, and educators are crucial. These stakeholders should provide guidance, address challenges, and ensure students achieve their learning outcomes.
Post-placement evaluations help assess the effectiveness of SWL. Feedback from students, employers, and educators is valuable for continuous improvement.
While SWL offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges. Identifying and addressing these challenges is essential for a successful program.
Finding enough suitable placements for all students can be challenging, especially in industries with high demand.
Ensuring that SWL aligns with current industry standards requires ongoing collaboration and updates to the curriculum.
Students may struggle to balance the demands of their work placements with their academic responsibilities. Proper scheduling and support can help address this issue.
Take the initiative to learn as much as possible during your placement. Ask questions, seek feedback, and actively participate in tasks.
In addition to technical skills, focus on improving your communication, teamwork, and time management abilities. These skills are highly valued by employers.
Keep a journal or log of your structural workplace learning activities. Reflecting on your experiences helps you identify what you’ve learned and how you’ve grown professionally.
Structured Workplace Learning is a transformative experience that prepares students for the workforce by combining academic learning with practical experience. It benefits students, employers, and the education system by fostering a skilled, confident, and industry-ready workforce. Despite its challenges, structural workplace learning remains an invaluable component of education, bridging the gap between theory and practice and setting students on the path to success.
Disclaimer:
The information presented on the VET Resources blog is for general guidance only. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee the completeness or timeliness of the information. VET Resources is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for the results obtained from the use of this information. Always consult a professional for advice tailored to your circumstances.
Ben Thakkar is a Compliance, Training, and Business specialist in the education industry. He has held senior management roles, including General Manager, with leading Registered Training Organisations (RTOs) and Universities. With over 15 years of experience, Ben brings extensive expertise across audits, funding contracts, VET Student Loans, CRICOS, and the Standards for RTOs 2025.
Ben Thakkar
By submitting this form, you agree to the VET Resources Privacy Policy.
Notifications